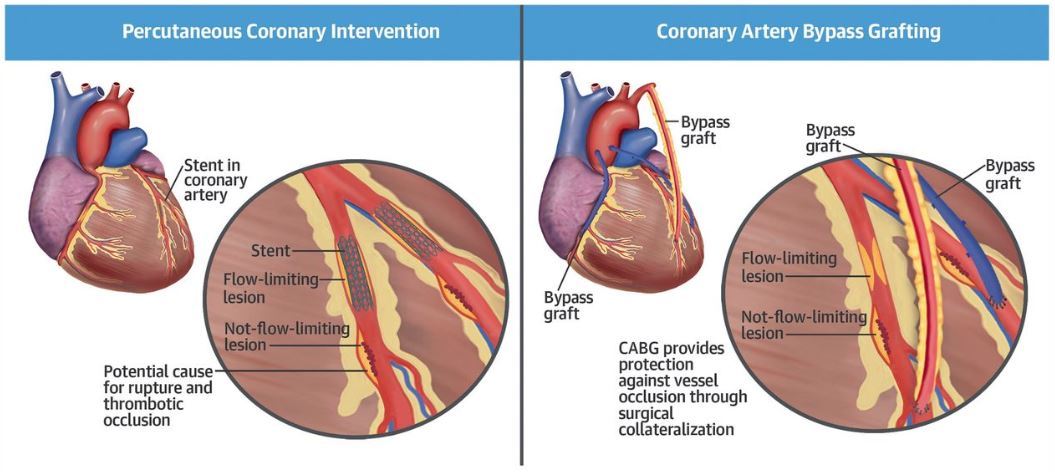
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) is an operation to treat angina and to reduce the risk of a heart attack. Angina is chest pain caused by low oxygen levels to the heart due to narrowing or blockages known as coronary artery disease. The aim of the operation is to restore the blood supply to the heart. With a successful CABG operation, most patients can expect a marked improvement in quality of life as well as increased life expectancy. The operation can be done using beating heart techniques as well as with the aid of a Heart Lung machine.
Five- and 10-year survival rates are ≈85% to 95% and 75%, respectively after successful CABG. A number of technical advances have improved short- and long-term outcomes as well as significantly reduced peri-operative morbidity, after coronary artery bypass grafting. These include off-pump and aortic no-touch procedures, use of multiple arterial grafts (Internal mammary artery and radial artery use), minimally invasive procedures, including robotic-assisted surgery and hybrid coronary revascularization.
CABG is superior than angioplasty in diabetic patients. patients with triple vessel disease when the left main coronary artery is involved. Long term survival benefits have been proven by multiple clinical trilas.
Coronary arteries are localized at the surface of the heart, that makes their access easy.
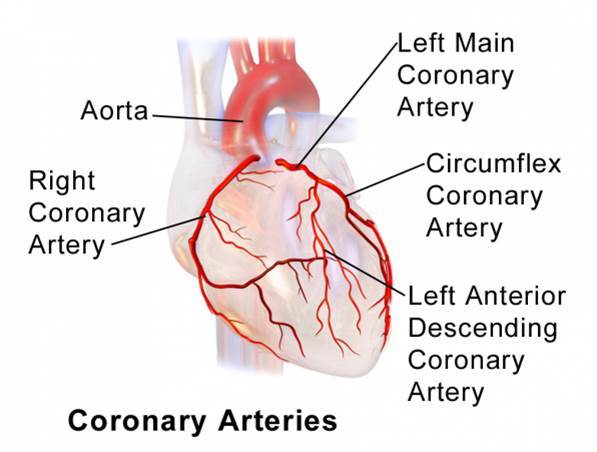
The goals of CABG are:
- Improving your quality of life and reducing angina and other CHD symptoms
- Allowing you to resume a more active lifestyle
- Improving the pumping action of your heart if it has been damaged by a heart attack
- Lowering the risk of a heart attack (in some patients, such as those who have diabetes)
- Improving your chance of survival
Conventional CABG is performed through a standard sternotomy approach and the operation is conducted under cardio-pulmonary bypass and arrested heart.
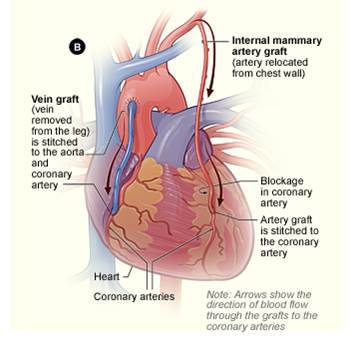
Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass (OPCAB) or Beating Heart Bypass Surgery is done on a beating heart using dedicated stabilizers; it lowers the risk of post-operative complications like stroke , atrial fibrillation , renal failure and pulmonary complications.